The monitoring function checks whether, for example, measured values fall below a certain minimum or exceed a maximum. Likewise, changes, plausibility, position (GPS) and differences can be monitored. Monitoring objects can be used to trigger events.
The configuration unit can only be used if the SCADA-Lizenz comprises the module "Extended events".
-
By selecting the "Monitoring" button, you can edit a monitoring operation that was created earlier. A new monitoring operation is created via the Plus button.
-
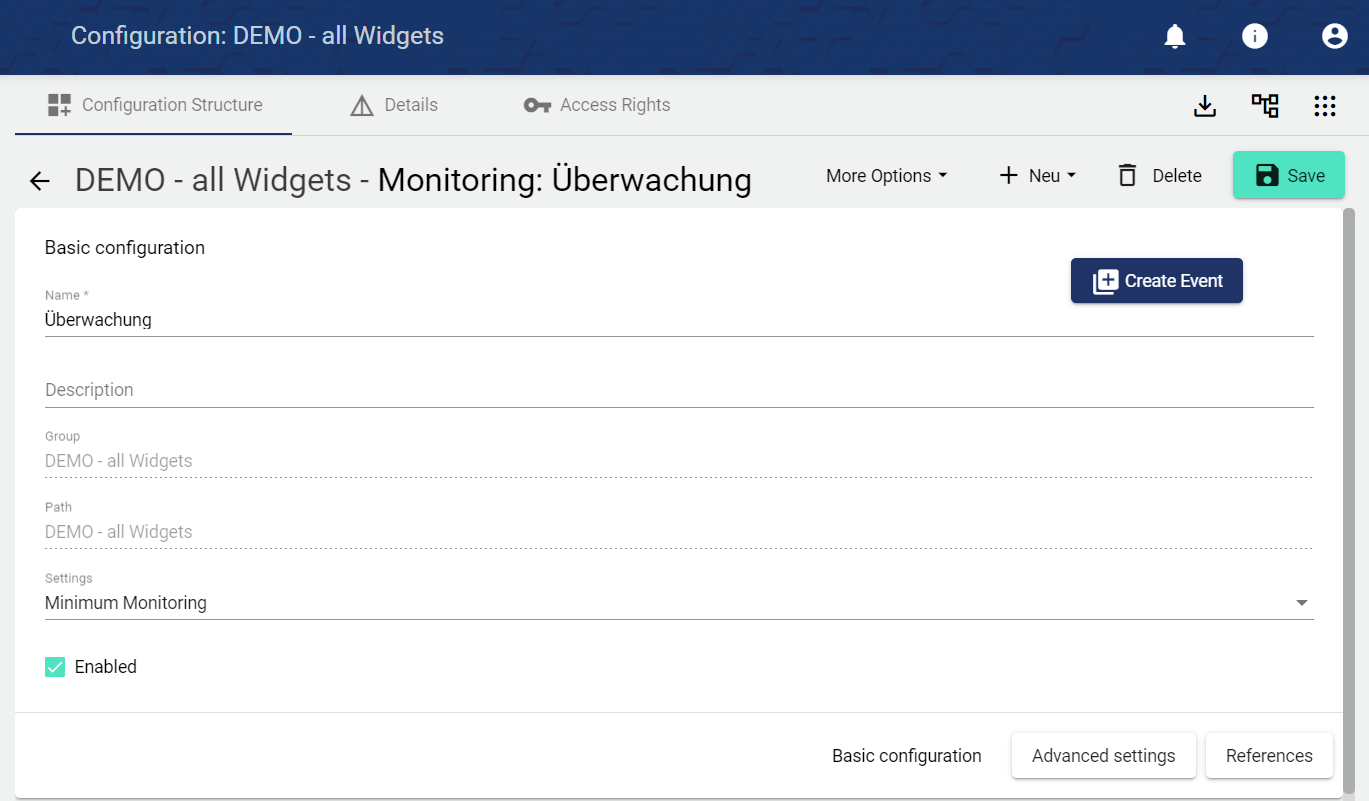
Assign the name of the monitoring operation in the Basic configuration. The Description field is optional. The "Group" field shows the Client in which the monitoring operation was created. The path is generated automatically by the system.
-
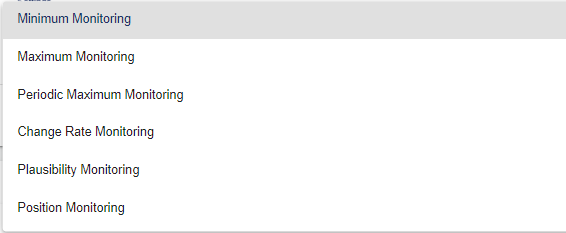
In the Settings field, select the Monitoring type.
-
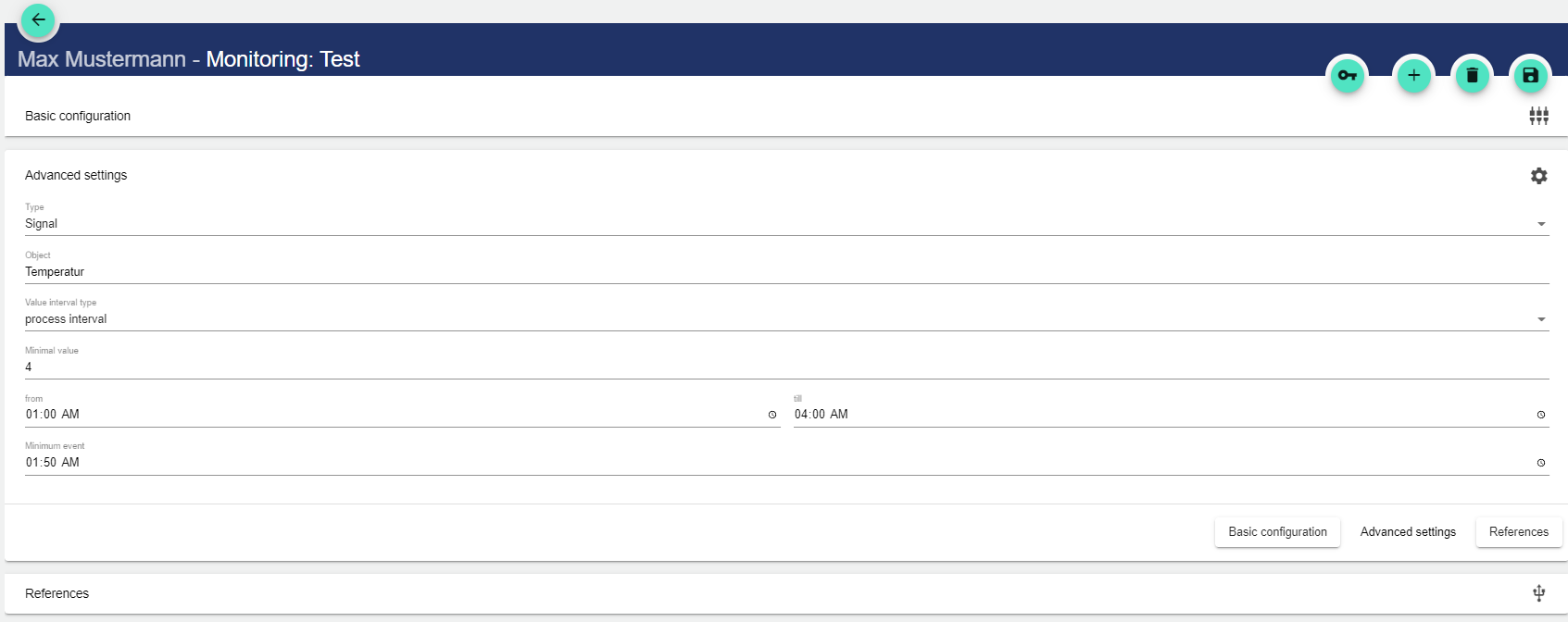
Minimum monitoring: Minimum monitoring: The signal values (or formula values) from the selected "Object" must have fallen below the set "Minimum value" in the time range (from ... till) at least once in the selected "Value Interval type" so that no event or alarm is triggered. However, if this minimum value is not fallen short of, a message or an event for an alarm is triggered.
The time window for the monitoring is defined by "from", "till".
The "Minimum event" specifies the time at which the event or alarm is to be triggered.
Example application: Alarm in the morning at 7 o'clock that no leakage has occurred during the night.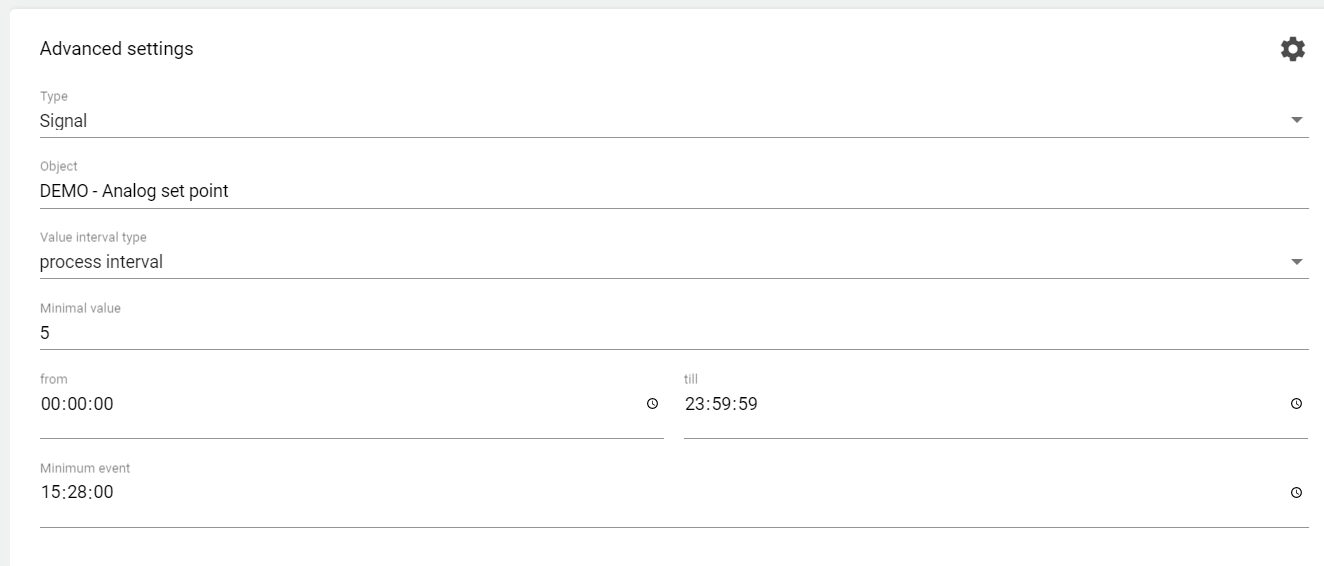
-
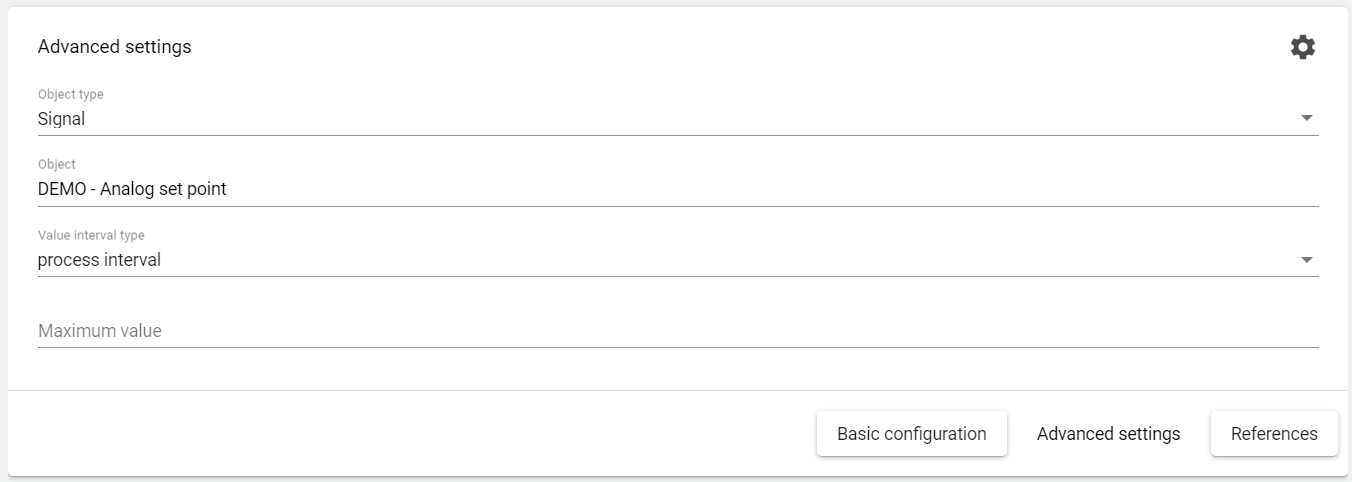
Maximum Monitoring: The signal values (or formula values) from the selected "Object" must exceed the set "Maximum value" in the selected "Interval type" so that an event or alarm is triggered.
-
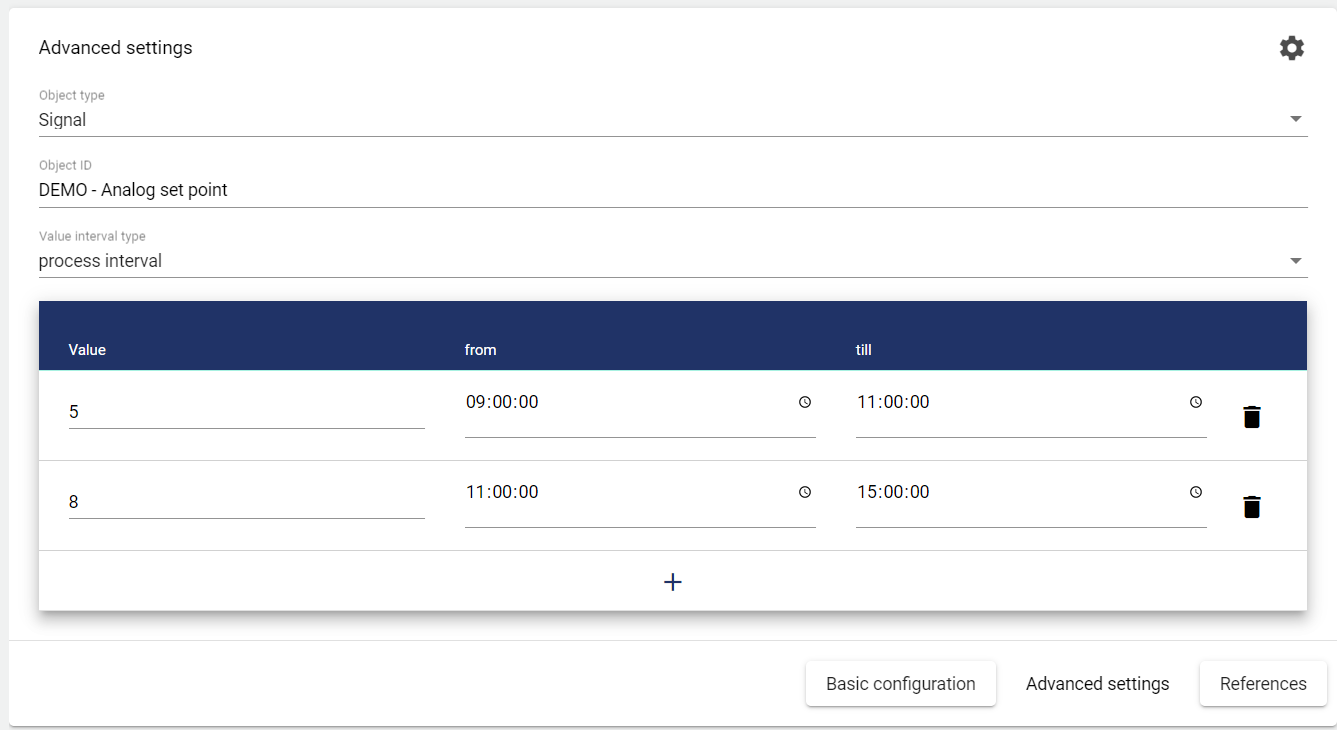
Periodic Maximum Monitoring: The signal values (or formula values) from the selected "Object" must exceed the set "Maximum value" in the selected "Value Interval type" in the respective time range (from ... till) so that an event or alarm is triggered. If one of these values is exceeded, the event or alarm is triggered.
-
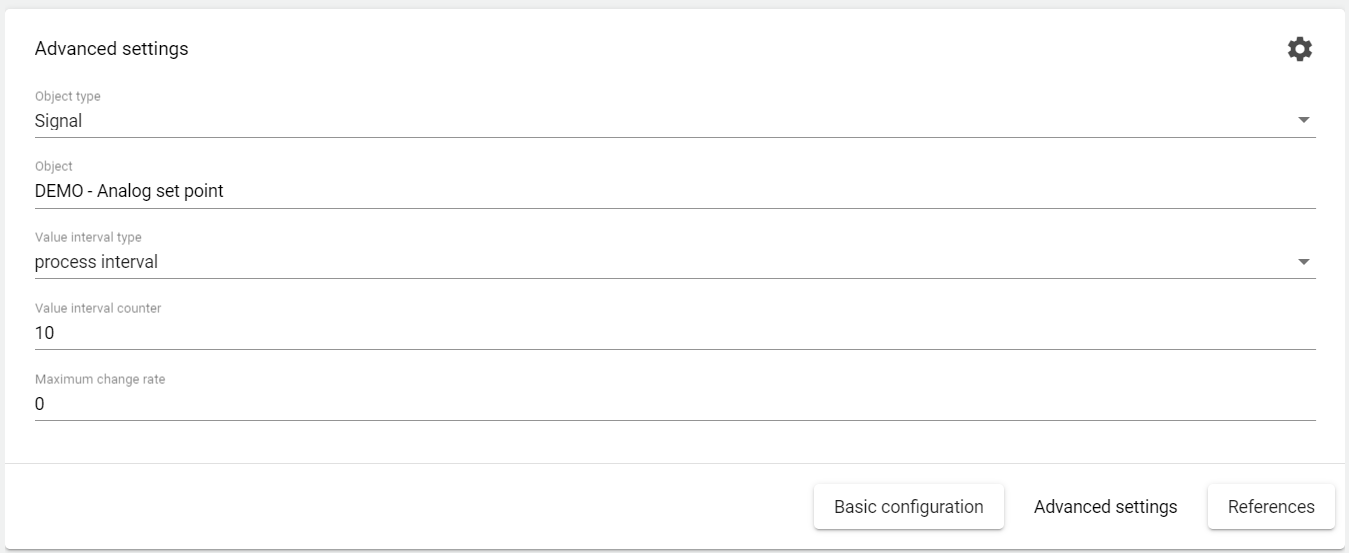
Change Rate Monitoring If the respective signal or formula (object) in the respective "Value interval counter" is exceeded by the "Maximum change rate", an event or alarm is triggered.
For example, if a value is recorded every 10 seconds (process interval = 10 seconds). If the value interval counter is set to 50 seconds and the maximum change rate is set to 3, the system checks 5 times within the period of 50 seconds (1 time every 10 seconds) whether the maximum change rate of plus, minus 3 has been exceeded.-
Value interval counter: Specified in seconds. Interval for checking the rate of change
-
Maximum change rate: Definition of the rate of change.
-
-
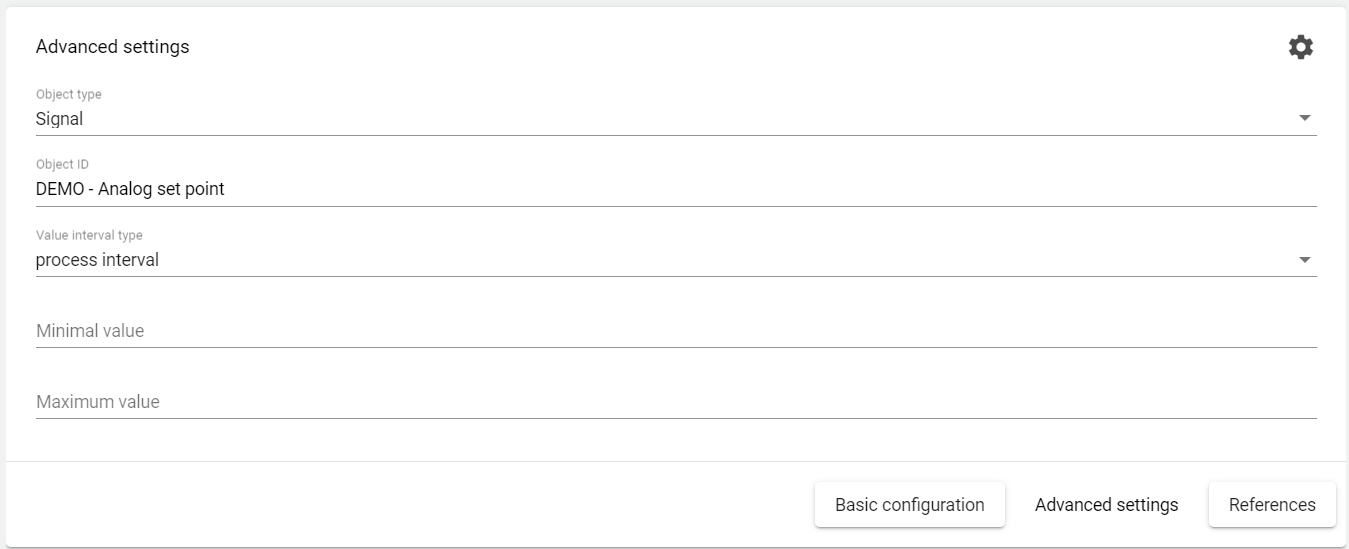
Plausibility Monitoring: The signal values (or formula values) from the selected "object" must remain in the selected "value interval type" so that no event or alarm is triggered. If the range (between min-max) is exceeded, this is triggered. This function ensures the verification of counters. Thus, failures of counters can be noticed more quickly.
e.g.: Production quantity à Daily interval between 1000 kg and 5000 kg à Check plausibility.
-
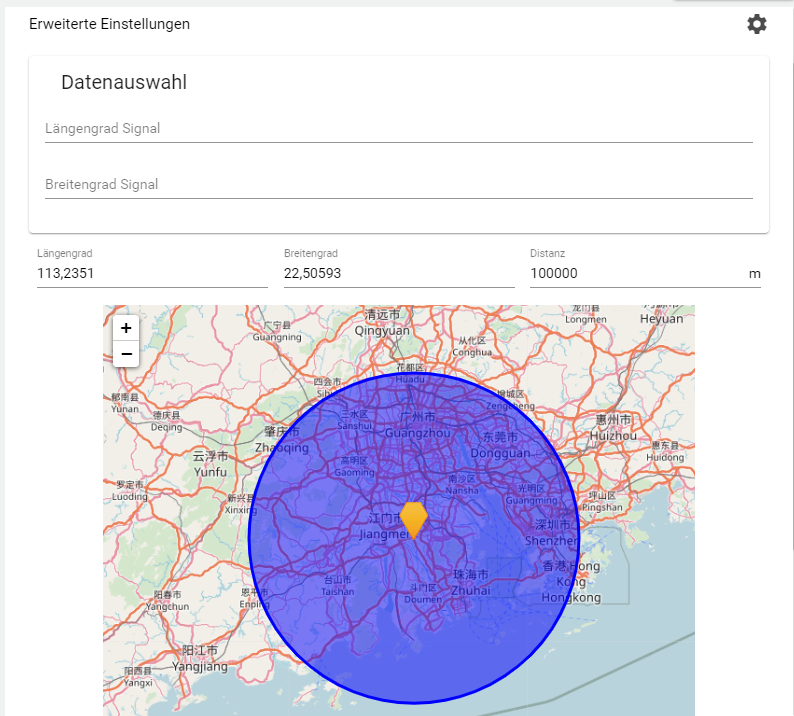
Position Monitoring: If the system (longitude-latitude signal) is outside the specified coordinates (longitude-latitude) including distance, a message for the alarm is triggered.
-
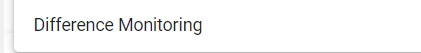
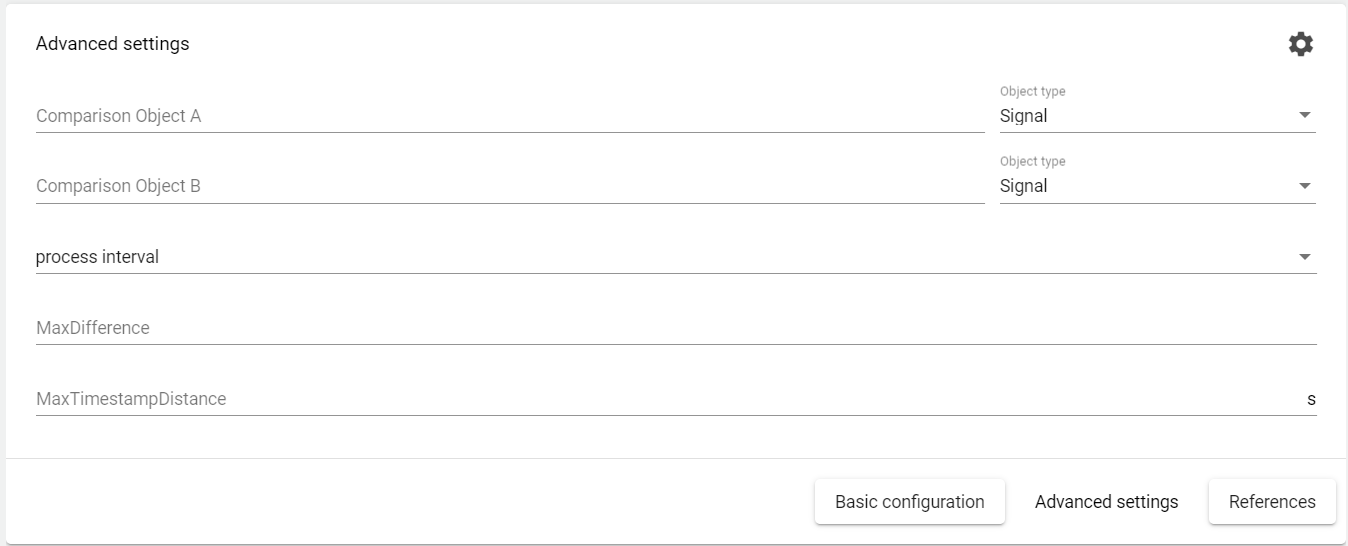
Difference monitoring: Comparison of two signals or two formulas.
→ MaxDifference: Definition of the max. difference.
→ MaxTimestampDistance: Input of time interval for the difference monitoring.
e.g. recording interval or process interval = 10 s with MaxTimestampDifference = 50 s. Then the difference is monitored over 5 process intervals. If the "MaxDifference" is exceeded once or several times within this period (e.g. these 5 intervals), an alarm or event is triggered.
-
-
The alarm schedule is activated or deactivated via the "Activated" checkbox.
Advanced Settings
-
Select type
-
Signal: Select a signal that was created for your system, whose value or coordinates are to be monitored.
-
Formula: Select a formula that was created for your system, which is to be executed.
-
-
Select the object in the system that is to be monitored.
-
Select the value interval type (see table "Possible interval types")
-
Specify the minimum value, the range of the value and the minimum result.
Possible interval types:
|
Interval Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Process interval |
The process interval corresponds to the interval set in the signal. |
|
Minor interval |
Equivalent to 15 minutes and is therefore the smallest interval. |
|
Hourly interval |
Equivalent to one hour and thus 4 times the minor interval. |
|
Two-hourly interval |
Equivalent to two hours and thus twice the hourly interval. |
|
Daily interval |
Equivalent to 24 hours and thus 12 times the two-hourly interval. |
|
Weekly interval |
Equivalent to 7 days (168 hours) and thus 7 times the daily interval. |
References
All references to this monitoring operation are displayed in the References.
